Aluminum is the third most prominent element in the earth’s crust. Due to its low density and other properties, it serves almost every industry. However, many people don’t know the exact density of aluminum and its alloys. This property is what makes aluminum popular.
So, what is the density of aluminum? How does this characteristic enhance its importance? If you don’t, fret not! This guide is going to be dedicated to the density of aluminum metal. You’ll understand all the basic concepts. So, let’s get started!
Overview of Density

Before I take you into details, let’s first understand the meaning of density. It is a technical term that indicates the mass of an object present in unit volume. In simple words, it is the space an object occupies in unit volume. Let’s understand this with a simple example.
Suppose you have a piece of iron and a plate. You place that piece on the plate. This space occupied by the piece of iron will be its density. If it occupies more space, it will have greater density, and vice versa. The weight and thickness are directly proportional to each other.
If iron occupies more space, it means it is heavier as well. Different types of units are used to indicate the density. Those include kg/m3 (SI unit) and g/cm3 (FPS unit). Usually, the density is represented by the Greek letter rho (ρ). So, now you understand density, let’s dive in and discuss the density of aluminum.
What is the Density of Aluminum and its Alloys?

Pure aluminum has a density of 2700 kg/m3 (SI unit) or 2.70 g/cm3. These measurements can vary in aluminum alloys. Remember, this range of density is considered small. Due to this smaller density, aluminum is lightweight compared to other elements.
Different factors can influence aluminum’s density. For example, if aluminum has small impurities, its density will not be the same as mentioned above. The density I mentioned above refers to the purest form of aluminum.
Generally, aluminum is utilized in alloy with different other elements. The alloy element makes aluminum more robust and gives it features. Keep in mind that those alloy elements have different densities. Therefore, the aluminum alloy will have different densities depending on the alloy.
Density of Aluminum Alloys
As I said, there are different aluminum alloys. Aluminum is generally used in its alloy form. The alloy element gives it different features needed for other projects. The standard alloy elements include copper, zinc, magnesium, manganese, and silicon.
These alloy elements have different densities. When alloyed with aluminum, those elements alter the densities of aluminum. Let’s have a view at the various aluminum alloys and their densities:
| Aluminium Alloy | Alloying Elements | Density (g/cm³) |
| Aluminum 1100 | copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, silicon | 2.71 |
| Aluminum 2024 | Copper, manganese, magnesium | 2.78 |
| Aluminum 3003 | Manganese | 2.73 |
| Aluminum 5052 | Magnesium, chromium | 2.68 |
| Aluminum 6061 | Magnesium, silicon, iron, copper, chromium, zinc, titanium | 2.70 |
| Aluminum 6063 | Magnesium, silicon | 2.69 |
| Aluminum 7075 | Zinc, magnesium, copper | 2.81 |
| Aluminum 5083 | Magnesium, manganese, chromium | 2.66 |
| Aluminum 2011 | Copper, bismuth, lead | 2.83 |
| 6060 | Magnesium, silicon | 2.70 |
As mentioned above, pure aluminum has a 2.70 g/cm3 density. However, different aluminum has slightly higher or lower densities in the table. Do you know why? I bet you know now! This is due to the presence of alloy elements.
Density Chart for Aluminum Alloys
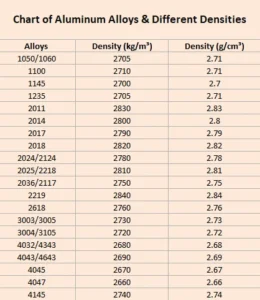
In the section above, I’ve mentioned aluminum alloys with their respective densities. However, there are countless types of aluminum present in the world. It is not feasible for me to write the density of each in one paragraph. Therefore, here is a visual chart showing the density of aluminum alloys.
How to Calculate the Density of Aluminum?
Calculating the aluminum’s density is very straightforward. You don’t even need a calculator. You simply have to know the formula used for density calculation. First, you note the mass in grams and aluminum volume.
If these two parameters are in place, all you need to do is to divide the mass by volume. This will give you the density of aluminum. If you are working with cm3, this will provide you with the density in g/cm3. If you work with m3, the density will be kg/m3. Here is the formula to use:
Density = Volume / Mass
By putting the values in this formula, you’ll be able to find the exact density of aluminum. Don’t be confused when calculating the densities of aluminum alloy. You can use this same formula to calculate their densities as well.
How Does Density Vary by Type of Aluminum?

Let me confuse you for a moment. The 1xxx series of alloys have a density very close to pure aluminum. Some other alloys have very high density. Examples include 7xxx or 8xxx series alloys. Moreover, some aluminum alloy series, such as 4xxx, have low density. Why is this so?
The question arises: Why is this difference, as aluminum is present in all alloys? This difference is due to the presence of alloy elements with different individual densities. In alloy series with high density, their alloy elements are weighty and dense, adding density to the overall alloy.
Similarly, the alloy elements in the low-density alloy series are lightweight. Remember that this variation in density follows in all aluminum alloys. No aluminum alloy has the same density 100% as pure aluminum.
How Does Aluminum Compare in Density with Other Metals?
Aluminum is lightweight, which is its top characteristic. Due to this feature, it is common in the aerospace and automobile industries. Being lightweight also means that its density (2.70 g/cm3) is on the lower side.
The density of aluminum metal is minimal compared to some of the metals. Here are some of the metals and their densities:
- Iron: 7.87 g/cm³
- Copper: 8.96 g/cm³
- Zinc: 7.14 g/cm³
- Lead: 11.34 g/cm³
- Titanium: 4.50 g/cm³
- Magnesium: 1.74 g/cm³
- Gold: 19.32 g/cm³
- Silver: 10.49 g/cm³
Looking at these metals, you will know how lightweight aluminum is. As you know, stainless steel is one of the prominent elements in metalwork. Aluminum’s density is 1/3 that of stainless steel. However, aluminum’s low density does not mean its low strength.
Aluminum is a solid metal. Its low light and high strength give you an excellent weight-to-strength ratio. Due to these characteristics, aluminum is the most demanded element used in metalworking.
Benefits & Features of Aluminum & its Alloy
It is no mistake that aluminum is one of the most used metals. The primary reason is its low density, which makes it very lightweight. Therefore, industries such as aerospace and automobiles use it.
The parts and components made with aluminum are lightweight. So, vehicles made with such parts consume less fuel. Similarly, such lightweight components are used in making the wings of airplanes. Let’s go down and further discuss the features of aluminum.
1- Resistance to corrosion
Aluminum makes oxide when it comes in contact with oxygen. So, parts made with aluminum become rustproof. When an aluminum part is used outdoors, it reacts with oxygen and forms oxides. This oxide acts as a protective layer. This protects aluminum parts from corrosion and other environmental effects.
This is the primary reason behind its extensive use in metalwork. The doors, windows, and parts used outdoors are made of aluminum and are durable. They require no maintenance except for a wipe now and then. Even in harsh rainy weather, these parts remain in good shape.
2- Recyclable
What makes aluminum a popular choice is its recyclability. It has the highest recycling rate of any metal. This means that aluminum can be reused and repurposed repeatedly. Recycling aluminum can save up to 95% of energy. This recyclability indicates that the aluminum is environment-friendly.
3- Durability & Strength
Aluminum is an essential metal due to its durability. The elements used in making aluminum allow it to have a long life, and the protective layer of oxide makes it rustproof. Many people consider aluminum a weak metal due to its low density. They are wrong.
Not only aluminum but all of its alloys are also solid. They demonstrate a promising weight-to-strength ratio. This makes aluminum an excellent choice for structural purposes. One of the strong aluminum alloys includes 7050 (with a density of 2.83 g/cm3). It is more robust than standard steel but only one-third of its weight.
4- Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Aluminum finds its application in making wires and power lines. Its high conductivity makes it an ideal choice for such purposes. Due to its excellent thermal conductivity, aluminum is also used in heat exchangers. Keep in mind that its thermal conductivity is higher than that of copper. However, its electrical conductivity is lower than that of copper.
5- Cost Effective
Aluminum is not very expensive. Its mining and refinement process is relatively more straightforward and less costly. This is what many manufacturers want. Every manufacturer aims to make a less expensive product. The usage of aluminum perfectly serves them. It also makes the final product less costly for consumers.
Conclusion
It is an undeniable fact that aluminum makes our lives possible. Many products around us are dependent on this metal. However, aluminum’s pure form is less common than its alloys. Such extensive usability of aluminum is due to its lower density.
This guide covers all the details about the aluminum alloys and their densities. In summary, aluminum is a very lightweight metal and is the heart of metalwork. At HXSCO, we work as an aluminum supplier. If you need aluminum, feel free to contact us.
